A large number of natural and technological processes involve mass transfer at interfaces. Interfacial properties, e.g., adsorption, play a key role in these processes. The mechanistic understanding of surface adsorption often assumes molecular diffusion in the bulk liquid and subsequent adsorption at the interface. Diffusion is well described by Fick’s law, while adsorption kinetics is less understood and commonly described by Langmuir-type empirical equations. In this study, a novel theoretical model for adsorption dynamics at the air-liquid interface is developed; in particular, a new kinetic equation based on the Statistical Rate Theory (SRT) is derived [1]. The developed mathematical model is then generalized by considering non-ideal surface behavior.
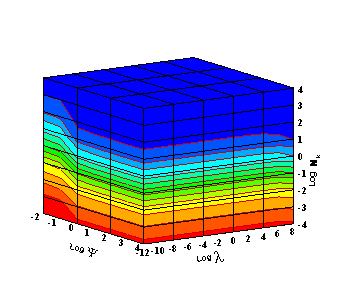
Figure 1: Simulation results using color contour show 3 different regimes of adsorption dynamics: blue - diffusion controlled, red - transfer controlled, and color transition from blue to red - mixed controlled.
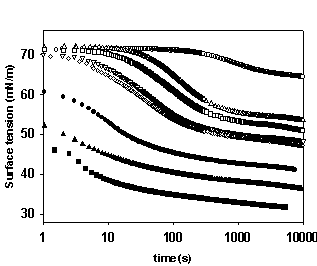
Figure 2: Dynamic surface tension of a nonionic surfactant at various solution concentrations. The lower surface tension value corresponds to higher concentrations.
Adsorption dynamics is governed by three dimensionless numbers [1]: y (ratio of adsorption thickness to diffusion length), l (ratio of square of the adsorption thickness to the ratio of adsorption to desorption rate constant), and Nk (ratio of the adsorption rate constant to the product of diffusion coefficient and bulk concentration). Numerical simulations for the surface adsorption are carried out, and three different regions of adsorption dynamics are identified: diffusion controlled, transfer controlled, and mixed diffusion-transfer controlled (Fig. 1).
The numerical simulations are validated using the literature reported and the experimentally obtained dynamic surface tension data. Experimental dynamic surface tensions are obtained using a pendant drop technique—Axisymmetric Drop Shape Analysis-Profile (ADSA-P) (Fig. 2). Dynamic surface tensions of a number of surfactants are measured and compared with the model.
[1] Biswas, M.E., Chatzis, I., Ioannidis, M.A., Chen, P. (2005). J. Colloid and Interface Sci. 286, 14-27.