Surface Characterization of Polymer in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
Supercritical fluids have been used in many fields such as the plastics, food, and pharmaceutical industries. Carbon dioxide has been one of popular substances in supercritical fluid technology. The understanding of fundamental properties of polymers in supercritical CO2 is essential to improve technology and energy efficiency. Specifically, the interfacial tension of polymer melts provides valuable information about polymer processes such as foaming, particle suspension, wetting, and polymer blending [1]. In this research, Axisymmetric Drop Shape Analysis-Profile (ADSA-P) is utilized to investigate interfacial properties of polymers in supercritical CO2. The objectives are: (1) to investigate surface tension behavior of polymers in superficial CO2 at various process conditions; (2) to optimize the process conditions in the microcellular foaming process; (3) to apply these techniques to polymer modifications (molecular weight, branch of polymers, crystalline and chemical additives).
[1] Park, H.; Thompson, R.B.; Lanson, N.; Tzoganakis, C.; Park, C.B.; Chen, P., J. Phys. Chem. B., 111, 3859 ( 2007).
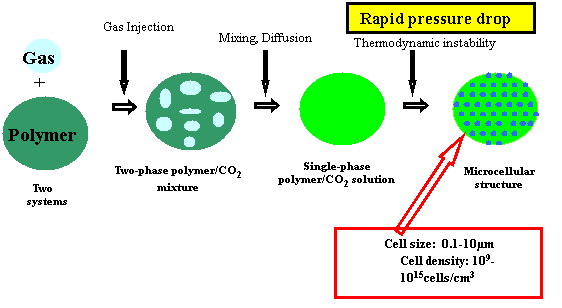
Application of polymer in supercritical carbon dioxide: Microcellular process